Hamas’ assault on Israel is aided by a coordinated influence operations campaign involving tens of thousands of fake profiles. In their efforts to gain worldwide public support, these fake profiles have been spreading propaganda, disinformation, and fake news to manipulate public discourse. Learn what Cyabra uncovered.
On 7 October, 2023, Palestinian militant groups, mainly Hamas, launched a major attack on Israel from the Gaza Strip. The attack included rockets and armed militants infiltrating across the border to Israeli communities. The first attack resulted in many casualties as well as hostages taken back into Gaza. In response, the government of Israel declared a state of emergency and war. While civilians on both sides suffer its consequences, another battlefront rages on social media platforms.
In the first two days of the war (October 7-9) Cyabra has analyzed 2 million posts, pictures, and videos across Facebook, X (Twitter), Instagram, and TikTok. The analysis identified tens of thousands of fake profiles spreading disinformation and propaganda, as well as gathering sensitive details about their targets. Here are some of our findings:
1. Conversations About the War Are Flooded With Fake Profiles
Cyabra scanned over 162,000 profiles that took part in online conversations about Hamas’s attacks and their aftermath. One out of four (25%) of those social media accounts taking part in the conversation about the war was identified as fake (40,695 profiles in total).
2. Those Profiles Spread Content Faster Than Ever Before
In just two days, the fake profiles posted over 312,000 pro-Hamas posts and comments. Some posted hundreds of times every day, meaning a new post every few minutes. The profile below, for example, posted 616 times in two days.
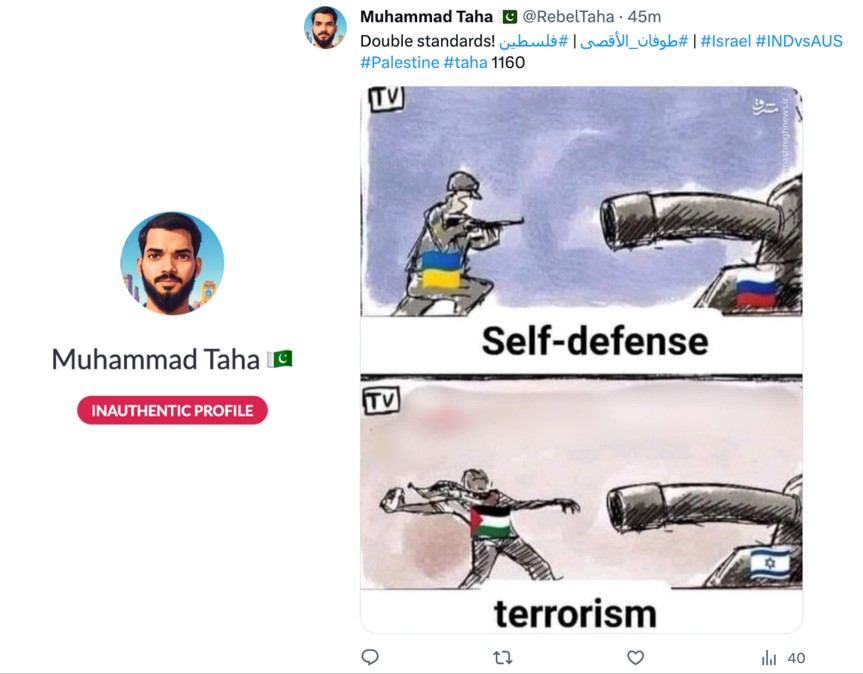
3. The Bad Actors Know How to Take Advantage of the Algorithm
Posts containing pro-Hamas propaganda actually used pro-Israel hashtags, such as #IStandWithIsrael or #Israel in order to gain higher exposure and reach new audiences.
The frequent posting and clever utilization of hashtags played a crucial role in the fake profiles’ propaganda going viral, resulting in over 371,000 engagements (replies and shares) and over 531 million views in just two days.
4. The Fake Profiles and Narratives Were Meticulously Crafted
The fake profiles that took part in the conversation were created beforehand, some over a year ago, but were made active only when the war started.
The narratives set by the bad actors were also planned in great detail, following a strategy to gain worldwide recognition and improve Hamas’s global image.
Cyabra detected three types of narratives in those trending posts:
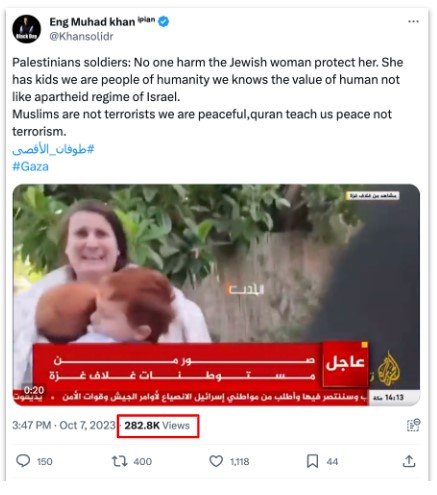
A. Hamas is merciful and humane towards hostages: As videos of Israeli women and children taken captive by Hamas started circulating, fake profiles declared no harm would come to them, explaining that Hamas was known for its humanity and compassion. The trending post below, which followed this narrative and included an image of a woman and her kids kidnapped into Gaza, reached over 280,000 views.
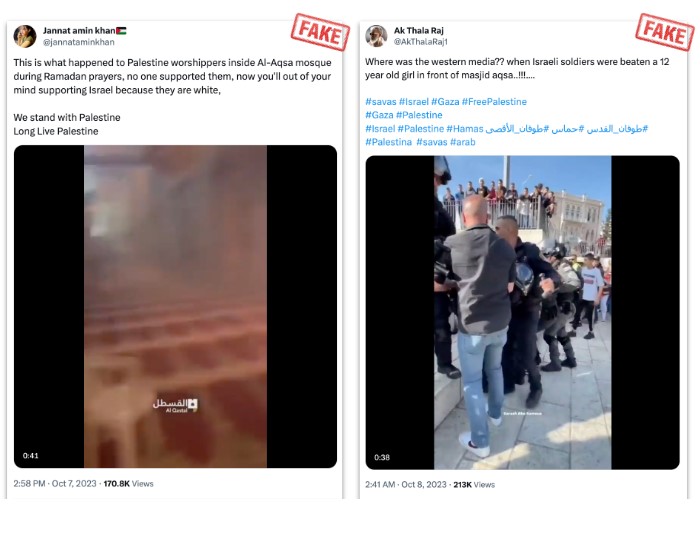
B. Hamas’s attack was a response to Israeli soldiers attacking Palestinians during prayer in Al-Aqsa mosque: Over 10,000 posts mentioned Israeli IDF soldiers attacking Israeli Arabs and Palestinian Arabs while they were praying in Jerusalem’s Al-Aqsa mosque, claiming Hamas’s attack on Israel was a direct response to crimes committed by Israel. This strategy was further strengthened by the fact that Hamas itself named its attack “Operation Al-Aqsa Flood”. Some of the posts shared videos and images, claiming they were recently taken. The posts that shared this narrative reached 7,686,000 views, reinforcing the legitimacy of Hamas’s actions against Israel.
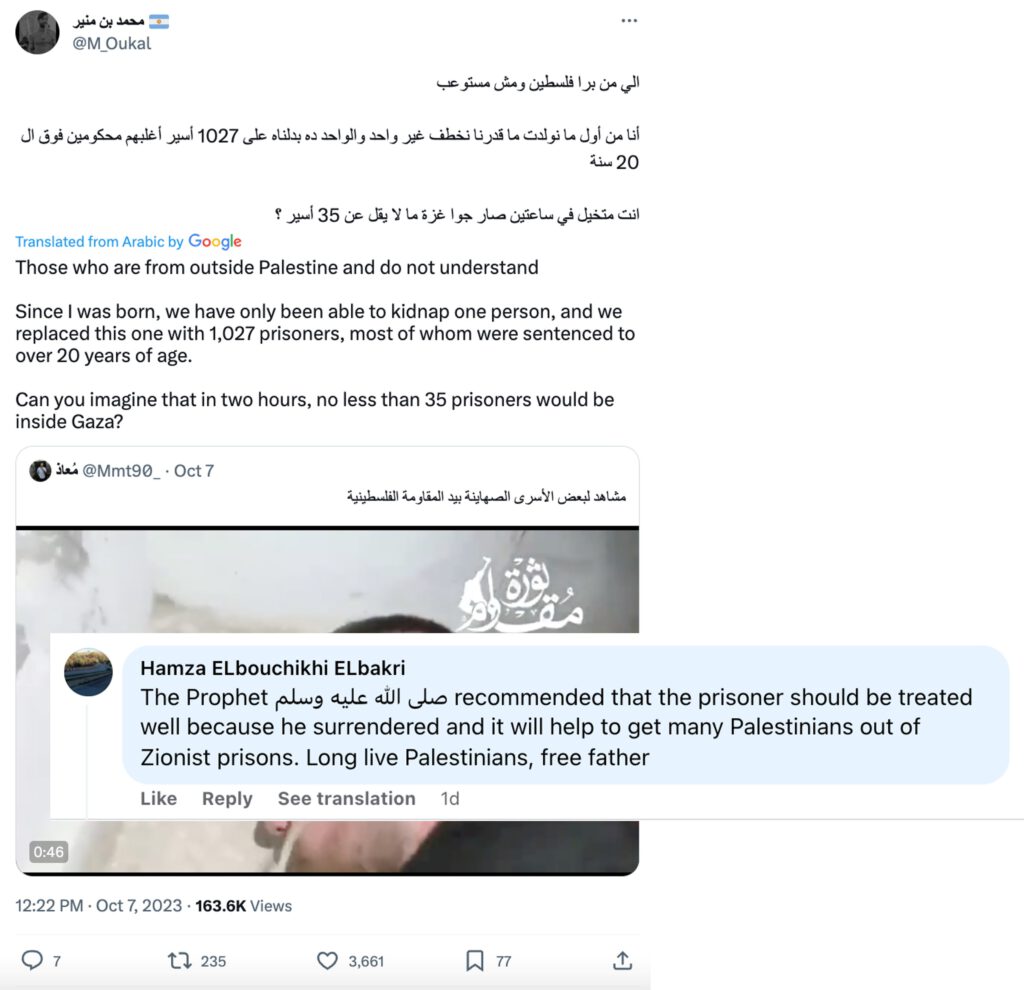
C. Kidnapping Israeli citizens into Gaza was necessary in order to start negotiations for the release of Palestinian prisoners sentenced to life in Israeli prisons: These posts discussed the Israeli hostages in Gaza as a potent bargaining tool, asserting that each captured Israeli held the value of hundreds and even thousands of Palestinian prisoners who, thus far, had no prospect of release, regardless of their offenses.
These posts served both as reinforcement to the idea that kidnapped Israelis would not be harmed as they are needed for prisoner exchange, and as a way to create the impression that the objective of Hamas’s attack was simply to set free Palestinian prisoners who had no other hope of freedom.
_______________
Disclaimer: Cyabra’s analysis is ongoing and new data will be coming in as the events continue to progress.