British supermarket chain Waitrose, with over 300 stores and £7 billion ($8.8bn) in revenue, is going through a significant brand reputation crisis online.
But how much of it is led by fake profiles?
Cyabra has identified a disconcerting 24% fake profiles in the discourse around #BoycottWaitrose and parent company #BoycottJohnLewis.
Here’s why this trend is a source of concern for any – and every – brand.
TL;DR?
- #BoycottWaitrose and #BoycottJohnLewis started trending on February 17.
- 24% of the profiles in the discourse were fake. Many of the fake profiles had a verification badge (the blue tick), which helped push their content.
- The fake profiles reached 1,446,000 potential views and 1,200 engagements.
The Colossal Impact of Fake Profiles
On February 14, Waitrose released a new magazine that included instructional articles for parents of transgender children, offering binders that can be purchased in their stores.
The hashtags #BoycottWaitrose and #BoycottJohnLewis started gaining momentum around February 15, reached X’s Top Trends on February 17, and peaked on February 18. Overall, in just one week, 831 profiles participated in the discourse, collectively sharing 1,298 posts and comments in just one week.
As mentioned above, 24% of those profiles (almost 1 in 4) were fake. As evident in the graph below, the fake profiles latched onto the hashtag only when it started trending but quickly caused a huge increase in virality, affecting authentic profiles.
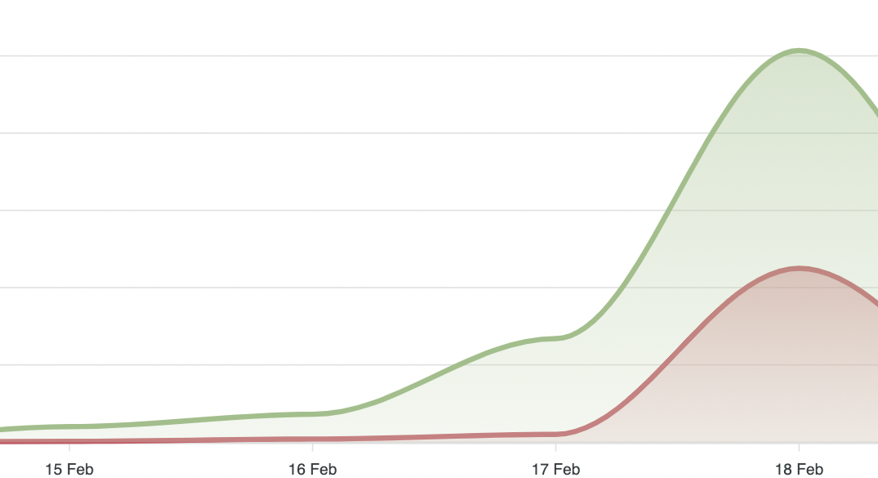
Fake profiles in those conversations achieved tremendous exposure, partly due to many of them acquiring the blue tick on X (verification badge, meaning a paid account), which helped their content reach a much higher exposure rate: overall, the fake profiles in the discourse reached a massive 1,446,000 potential views and 1,200 engagements.
What Are the Bots (Not) Selling?
Bot networks can be purchased and leveraged against companies and utilized for a fake campaign directed to harm brand reputation. This tactic has been used by competitors, enraged customers, or even foreign bad actors seeking to harm a national enterprise company.
This was not the case here.
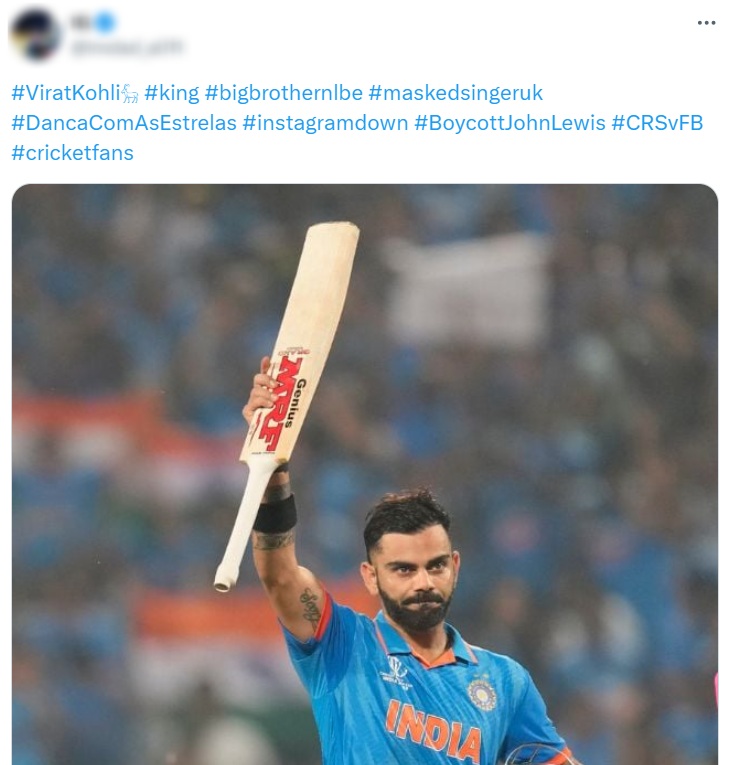
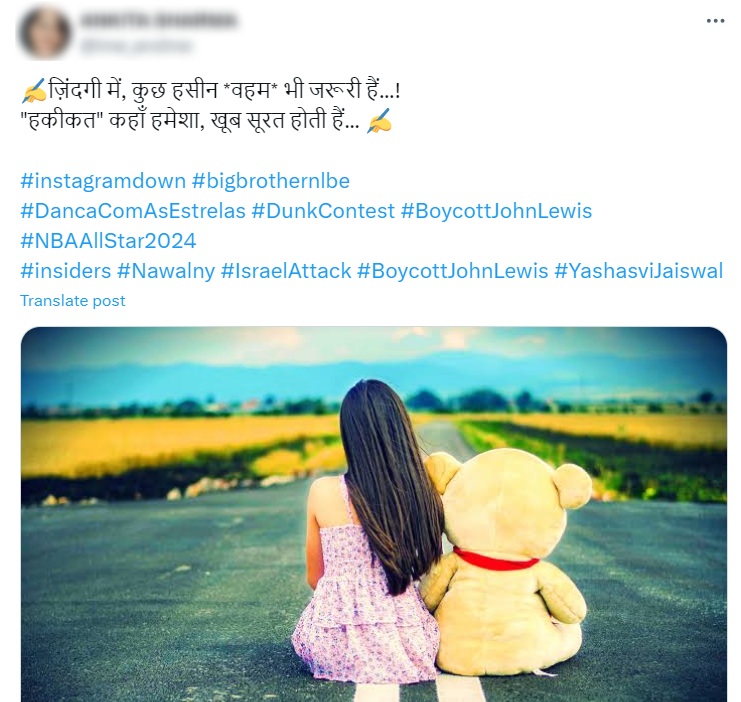
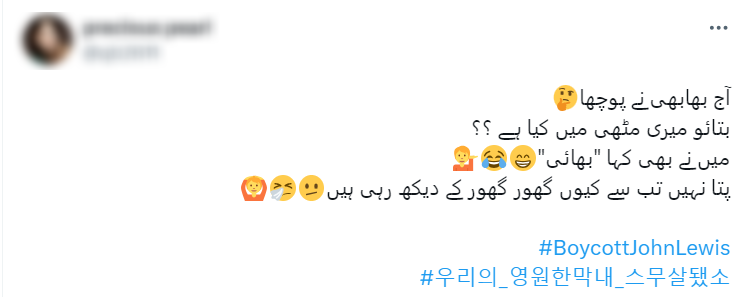
The boycott hashtags against Waitrose and John Lewis started organically, but when they started trending, they were latched onto by bots that were created to promote completely different topics. Actually, most of them weren’t even promoting those topics yet – since most of them were relatively new, created between November 2023 to January 2024, they were just using the hashtags while they were building their credibility and activity history, as can be seen in the example below – notice the blue tick in the first profile, and the other hashtags that were used in all three posts, all having nothing to do with the images or texts posted.
The wide spread of the bots as well as the purchased blue ticks also helped the fake profiles integrate themselves into authentic conversations. The image below shows the communities of authentic profiles around the hashtags, and how bots managed to effectively engage and interact with real accounts.
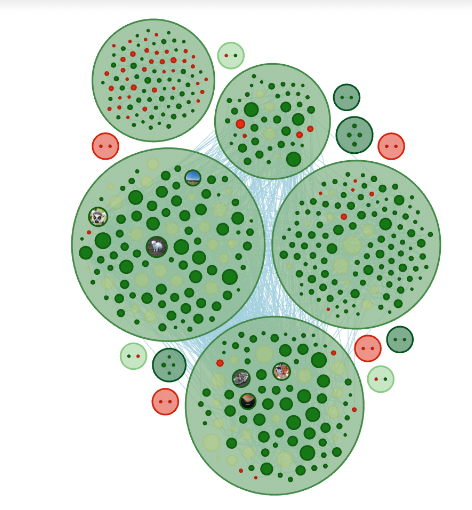
In the end, it didn’t matter that the bots themselves were not actually discussing the brand, or even spreading negativity – because they latched onto negative hashtags. The boycott hashtags trended wildly, harming the reputation of Waitrose and John Lewis.
This tactic of fake profiles scanning the most viral hashtags in every country and using them to reach a wider audience – or in other words, using trending hashtags to promote completely unrelated topics – is on the rise in recent months, and has already damaged huge brands such as Ripcurl, Zara and Bolt.
This tactic demonstrates a new threat to the world of marketing, PR and communications, particularly when it comes to leading brands. This is why identifying fake profiles and detecting their effect on the conversation requires introducing our marketing teams and agencies to new technologies and tools. If you’d like to learn more, contact Cyabra.


