TL;DR
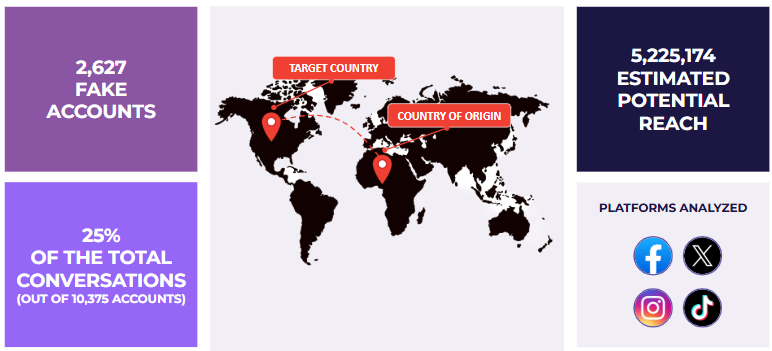
- Cyabra uncovered a sophisticated Nigeria-based influence operation: 2,627 fake accounts infiltrated authentic US conversation clusters
- Unlike typical influence campaigns, these fake accounts had massive success impersonating real accounts, and their content was widely shared by real people
- The operation generated 13,600+ engagements and reached an estimated 5.2 million views by successfully infiltrating legitimate discourse
- High-impact tactics included prompting authentic accounts (including one with 74,000+ followers) to reshare manipulated content, creating the illusion of widespread Nigerian calls for US intervention
- The operation employed distributed assets operating from multiple countries using VPNs to coordinate messaging, demonstrating advanced infiltration tactics commonly seen in state-backed campaigns
Here’s What Cyabra Uncovered
In November 2025, Cyabra analyzed social media conversations about US-Nigeria relations across Facebook, X, Instagram, and TikTok. The findings were alarming: 2,627 profiles, which were 25% of the accounts in the conversation, were fake accounts participating in a coordinated influence operation. These inauthentic profiles generated over 13,600 engagements and reached an estimated 5.2 million potential viewers.
Unlike typical influence operations that operate in isolation, these fake profiles strategically integrated within authentic discussion clusters and engaged directly with real users. This direct engagement generated over 13,600 engagements and reached an estimated 5.2 million potential viewers, demonstrating sophistication closer to tactics previously associated with state actors like Iran and Russia.
Infiltration Strategy
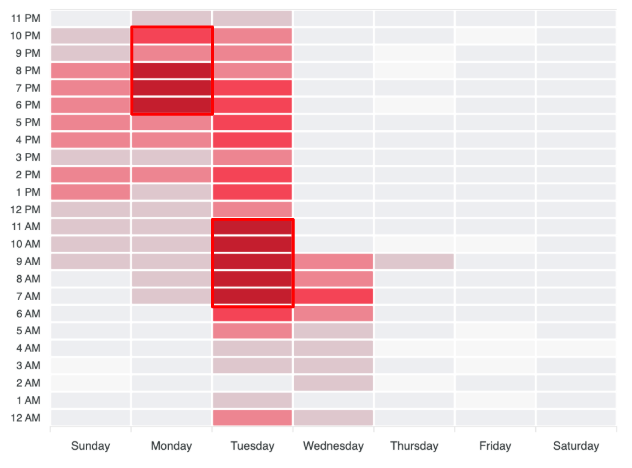
Cyabra’s analysis identified synchronized posting within identical timeframes, with visualization data showing clear bursts of activity by fake profiles operating during the same time periods, a hallmark of centrally coordinated influence campaigns.
The operation exhibited distinct, synchronized activity patterns from November 1 to 26, with posting times carefully aligned to match the authentic users’ engagement rhythms. This synchronization helped fake profiles blend seamlessly into ongoing discussions. The operation was particularly active on X, where it had the most significant impact.
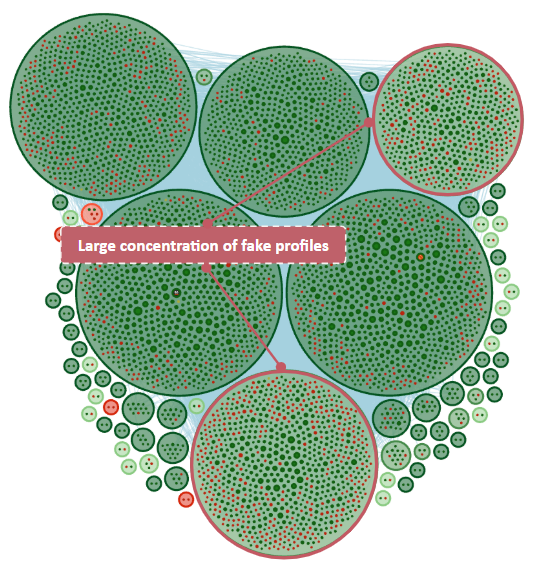
Beyond the Echo Chamber
What sets this operation apart is its approach to infiltrating authentic conversations. Rather than operating in isolated echo chambers, these fake profiles positioned themselves within genuine discussion clusters.
Cyabra’s analysis identified several coordinated behaviors indicating a centrally guided operation:
- Non-human and AI-generated profile images
- Repetition of similar messaging patterns
- Synchronized activity windows aligned with authentic users
- Emotionally charged language designed to provoke reactions
While the operation originated from Nigeria, many accounts operated from other countries, including the United Kingdom. This demonstrates a multi-source fake network employing VPNs and distributed assets, tactics commonly associated with state-backed campaigns.
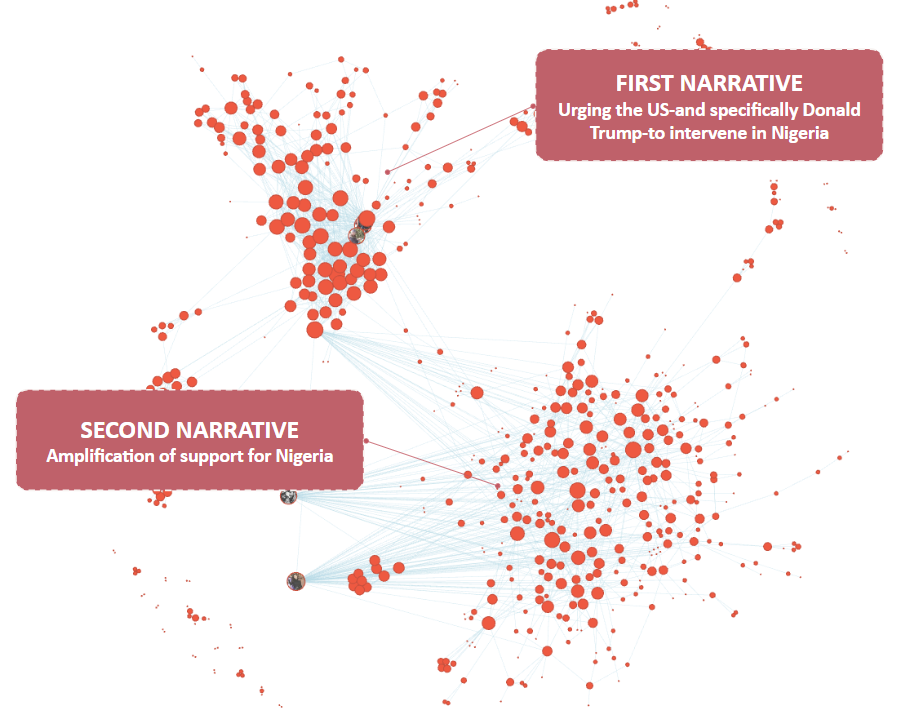
Engineered Narratives and Their Impact
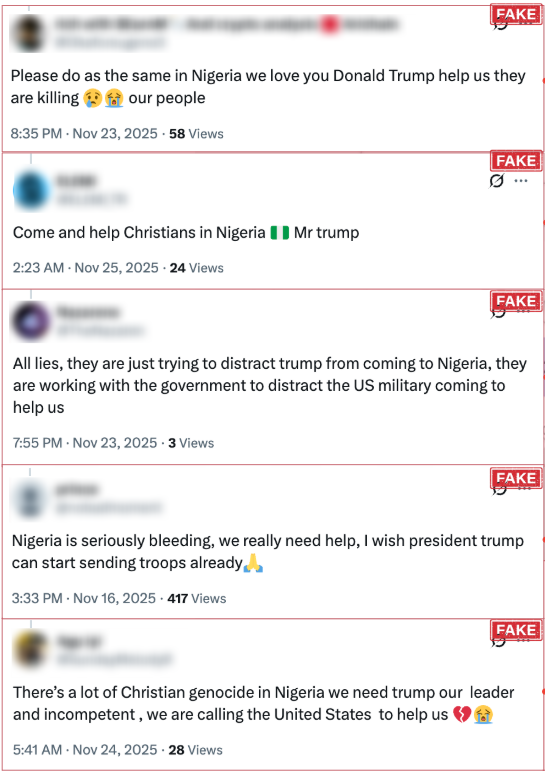
The fake profiles consistently amplified two central narratives:
- Urgent calls for US intervention in Nigeria, framed around Christian persecution
- Broad appeals to “support Nigeria” reinforcing the intervention narrative
These narratives created the appearance of widespread Nigerian support for US involvement. The most significant impact occurred when authentic users amplified content from fake profiles. In one example, a fake profile named “KelzOnyenkwere” posted a message urging former President Donald Trump to “save Nigeria from genocide.” While this post initially received modest engagement (350 views, 6 likes, 3 shares), it was reshared by Deacon Nick Donnelly, an authentic account with over 74,000 followers, thereby exponentially increasing the reach of the manipulated narrative.
This pattern of authentic amplification created the false impression that large numbers of Nigerian citizens were urgently calling for US intervention.
Implications for National Security
This influence operation poses significant challenges for government agencies. By infiltrating authentic conversations and spreading the campaign’s content through authentic influencers who unknowingly echoed and shared fake profiles, these manipulators created a sophisticated threat to public perception.
A comparison with other campaigns highlights these advanced tactics. While operations like China’s efforts targeting Taiwan rely on clusters of fake accounts interacting primarily with one another, the Nigeria operation’s strategic infiltration into real user networks represents an evolution in influence operation tactics. The manufactured appearance of grassroots consensus poses real risks to informed policy-making around US-Nigeria relations.
Detecting Embedded Influence Operations
For government agencies, this operation highlights the need for enhanced detection capabilities that go beyond content analysis to identify critical network behaviors. Key protections should include:
- Network analysis to identify fake profiles embedded within authentic conversations
- Behavioral pattern recognition to detect synchronized posting
- Cross-platform monitoring to track coordinated campaigns across social media
Cyabra’s AI-powered platform exemplifies this approach by analyzing posts, conversations, and cross-platform behaviors to categorize content by narrative, sentiment, authenticity, and coordinated activity, enabling precise detection of influence operations before they significantly impact public discourse.
As these operations evolve, government agencies must adapt their strategies. This Nigerian campaign serves as a critical case study for understanding how influence operations continue to evolve and why detection methodologies must similarly advance to protect the integrity of public discourse. Contact Cyabra to learn more.
Test Yourself: Identifying Influence Operations Tactics
* Coordinated posting patterns – Synchronized activity bursts occurring within identical timeframes
* Visual anomalies in profile images – using images of pets, landscapes, objects, or AI-generated faces
* Behavioral inconsistencies – Repetition of similar messaging and keyword patterns across the network
* Network structure analysis – Mapping how fake profiles positioned themselves within authentic conversation clusters
Network behavior analysis – Map relationships between accounts to identify infiltration patterns
Cross-platform monitoring – Track coordinated activity across multiple platforms
Enhanced public-private partnerships – Improve coordination between intelligence agencies and platforms
Real-time detection systems – Deploy monitoring tools that identify suspicious activity as it emerges
Infiltration of authentic clusters – Rather than operating in isolation, fake accounts strategically integrate into genuine discussion groups to engage real users directly.
Authentic amplification – The goal is to prompt high-follower, authentic accounts to reshare manipulated content, giving it unearned credibility and exponentially increasing its reach.
Sophisticated personas – Using GenAI to create consistent, high-realism backstories, including profile images and long social histories, to avoid easy detection.
Distributed assets – While originating in Nigeria, the network used VPNs to operate from multiple countries, including the UK, to mask its source.
Mimicking state actors – The coordination and scale of the 2,627 fake accounts demonstrated a level of sophistication typically reserved for state-backed entities like Russia or Iran.
Engineered grassroots consensus – By flooding narratives with “urgent calls for intervention,” the operation created a false impression of widespread local support for specific US foreign policies.


