On February 22, a cellular outage spread through the US.
Over 70,000 customers were left with no cell services for almost a full day. The companies whose customers were harmed the most were AT&T, T-Mobile, Verizon, and Boost Mobile, but other networks suffered from the outage as well.
In an era where most of us are addicted to our phones, and Americans check their phones an average of 144 times (techjury.net), one would expect this forced break to bring an online rage toward cellular providers (at least once the customers get back their access to the internet).
This, however, was not the case here.
Or, actually, it might have been – but any online rage was completely drowned out by a wave of positive discourse led by fake profiles that were praising some of the companies that were harmed by the outage.
Why was this happening, and more importantly, what’s so bad about bots sharing positive content about your brand?
TL;DR?
- On the day of the outage, 18% of all content related to it on X (Twitter) was generated by fake profiles.
- In conversations about T-Mobile, 19% of the profiles were fake.
- In conversation about Boost Mobile, 30% of the profiles were fake.
- The fake profiles promoted positivity towards the cellular brands, and criticized competitors suffering from the outage. A lot of the positive content was based on false facts.
Bots Don’t Care About Cellular Outage
The outage started around 2 AM on February 22. Since its source was unknown, it quickly led to a massive wave of misinformation and conspiracy theories online. At the beginning of this crisis, authentic profiles were promoting conspiracies and fake news, accusing everyone of the outage – from independent hackers to China, Russia, Homeland Security, and, of course, aliens. The FBI quickly reported it was investigating this crisis.
Check out some of the conspiracy theories that were spreading online, reaching massive exposure:
By the time it became clear the outage was not caused by a cyber attack or any other foreign influence, conversations about telecom companies were already trending, picked up by fake profiles.
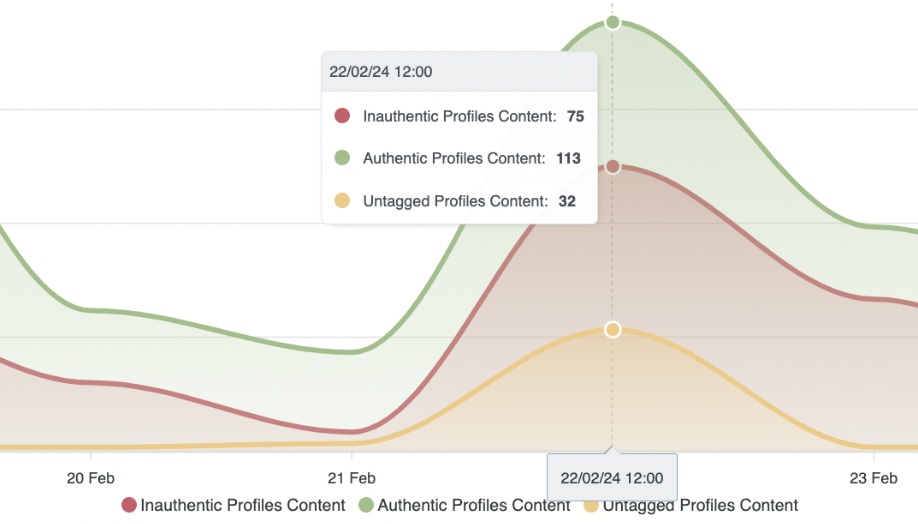
This was when fake profiles started promoting positive messages: In conversations that mentioned T-Mobile, 18% of the profiles were fake. In conversations about Boost Mobile, 30% of the profiles were fake. The fake profiles were either complaining about their cell company and saying they were going to switch to T-Mobile or Boost Mobile, or they presented themselves as customers of T-Mobile and Boost Mobile while claiming that the companies didn’t experience the outage at all. They also mocked competitor companies such as AT&T, Verizon, and others.
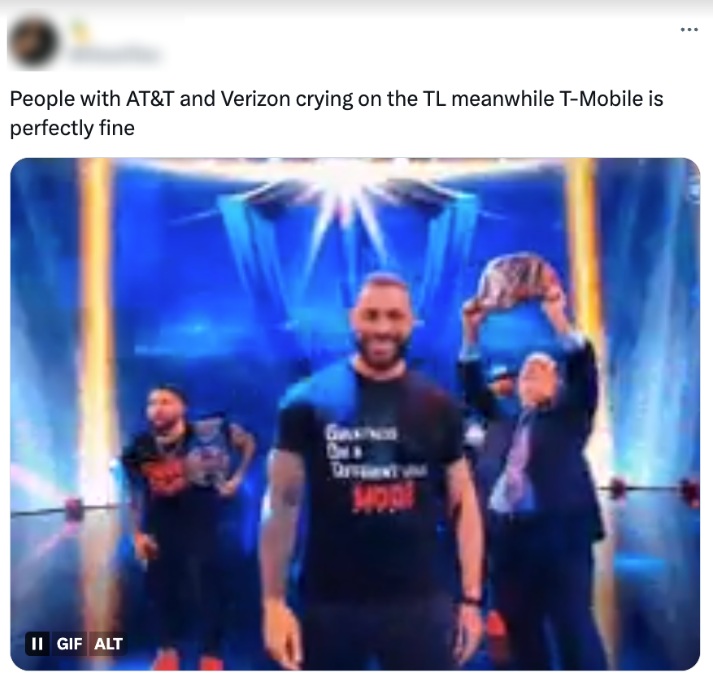


Fake profiles praising T-Mobile and Boost Mobile. The profiles were most active during hours of peak conversations by authentic profiles.
What’s Wrong With Bots Singing Your Praise?
In reality, T-Mobile and Boost Mobile suffered from the outage just as much as their competitors (T-Mobile even more than some). Keep in mind: it is very unlikely that T-Mobile and Boost Mobile were behind the bots spreading positive content about them. When dealing with PR crises, no marketing team will see a fake positive campaign as a legitimate method of response. When a cell company is in the midst of severe network problems, the time and headspace allocated to dealing with the emerging PR crisis will be used to spread reassuring messages, respond to angry customers, and explain that the technical issues will soon be resolved.
However, when fake profiles praise a brand, they usually do it using unreliable, incorrect, or just negative content, like claiming a company experienced no outage, or bashing competitors for suffering from the very same issues. In this case, it is more likely to assume that bad actors used fake profiles to spread anger, confusion, fake news, and mistrust. Boost Mobile and T-Mobile were just their chosen target – and none of them would be too happy with how bots sang their names using false content. It also stands to reason that bad actors chose the outage as a topic particularly because the conversations about it included a high volume of fake news and conspiracy theories.
This recent cellular outage and its online effect show how easily fake profiles can latch onto trending topics and harness them for their own agenda. It stresses the importance of identifying fake profiles and understanding their tactic, which requires supplying marketing teams with new technologies and teaching them new techniques. If you’d like to learn more and help your marketing team or agency, Contact Cyabra.


